Thyroid nodules are lumps that form on the thyroid gland. They are either solid (made of tissue) or filled with fluid. While thyroid nodules are quite common, most are found to be benign (non-cancerous) and do not require treatment. However, in cases where benign thyroid growths cause discomfort, difficulty swallowing or breathing, or cosmetic concerns, treatment may be considered. UVA interventional radiology offers thyroid nodule ablation as a minimally invasive treatment option for benign thyroid nodules.
Article Reviewed by Dr. Auh Whan Park
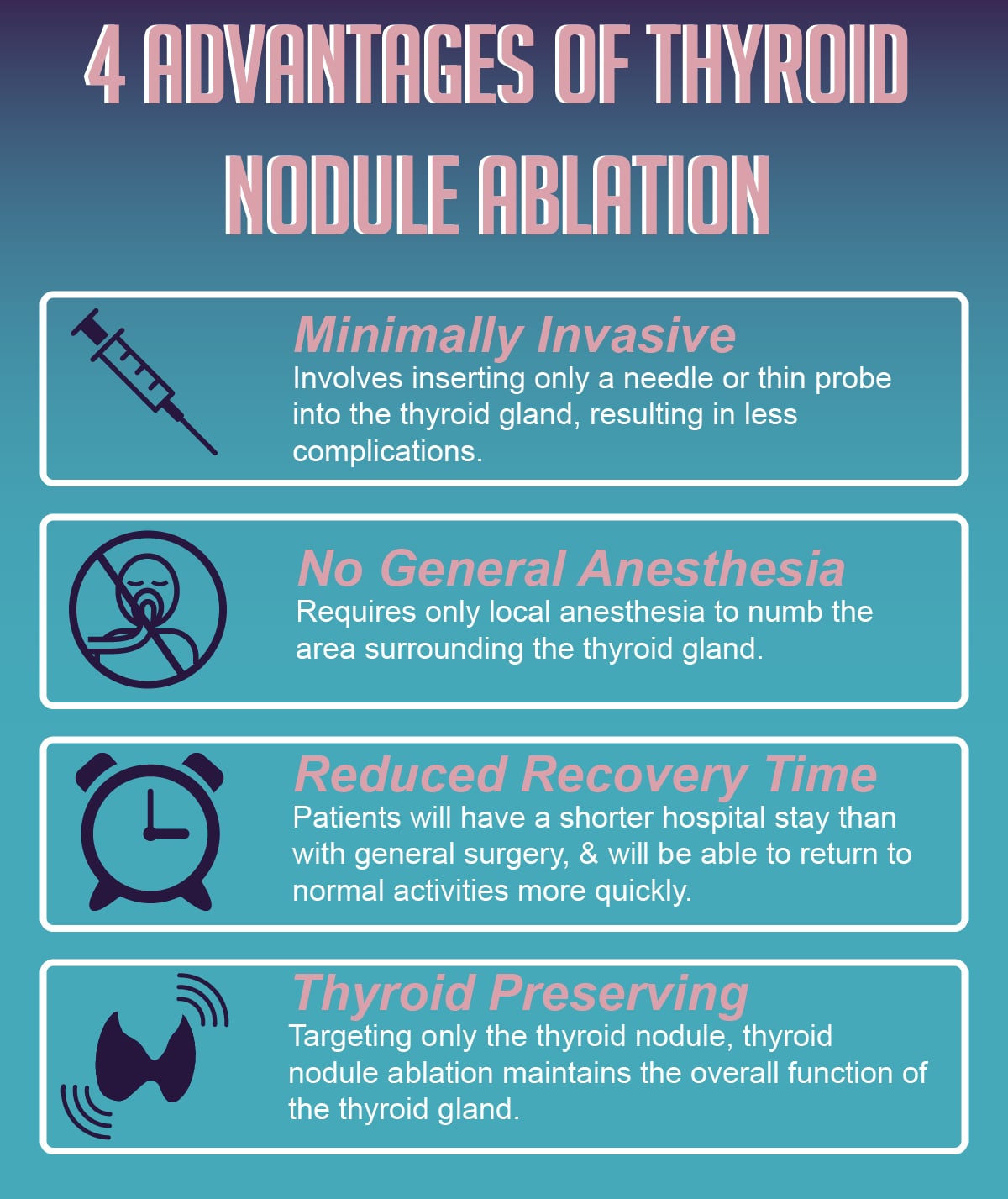
Advantages of Thyroid Nodule Ablation
Symptomatic thyroid nodules have typically been treated throughout the US with open surgery. However, surgery may have disadvantages and inherent risks such as the use of general anesthesia, scarring, hyperthyroidism, and long recovery times. This has led many physicians and specialists to question: is there a less invasive alternative to treating benign thyroid growths?
Thyroid nodule ablation has been performed widely in countries outside of the US, and has been shown in many clinical trials to be a safe, effective, less invasive procedure for patients with clinical symptoms or cosmetic concerns. Because of this, the US is now adopting this method of treating thyroid nodules. Thyroid nodule ablation has proven to be a good alternative for patients who are not able to undergo surgery due to other health conditions. It has even been shown to be an effective supplemental treatment for those with recurrent thyroid cancers.
Thyroid nodule ablation has advantages over surgery as it involves fewer complications, shorter hospital stay, requires only local anesthesia, and is thyroid preserving— meaning it is more likely to retain the overall function of the thyroid gland. This procedure has also been shown to greatly decrease the size of thyroid nodules, up to 93.5% during a 4 year follow-up period.
How It Works
Before performing the ablation procedure, the thyroid nodule is diagnosed and examined to determine if the growth is cancerous or benign. You and your doctor will discuss whether thyroid nodule ablation is right for you.
Interventional Radiologists perform thyroid nodule ablation by inserting a needle or probe directly into the thyroid nodule through the skin. Doctors are able to guide the needle or probe into the nodule using ultrasound imaging.
When this procedure was first being performed, radiologists used a chemical called ethanol to dehydrate and destroy the thyroid nodule. At UVA, interventional radiologists are now able to use thermal energy (heat) conducted through a special probe to effectively destroy the nodule. This technique has shown to be more efficient for solid nodules, & better preserves the entire thyroid gland.
UVA Interventional Radiology is one of the first in the US to offer thyroid nodule ablation using thermal energy, and it is now considered a top alternative treatment for benign thyroid nodules. The skilled interventional radiologists at UVA provide this procedure as a less-invasive, safe, effective option for patients who deal with symptoms from thyroid nodules, have cosmetic concerns, or who may not be eligible for traditional surgery. If you suffer with a thyroid nodule, talk to your doctor about a referral, or call 434.924.9401 to request a consultation with a UVA Interventional Radiologist.