Many people have heard of varicose veins in the legs, but did you know that a similar vein condition can occur in men within the scrotum? Varicoceles are enlarged, failing veins in the scrotum that can cause daily discomfort such as aching and swelling in the testicles. At UVA Interventional Radiology, we want you to be aware of the minimally invasive treatment option we provide for varicocele.
Article Reviewed by Auh Whan Park, MD
Varicocele: What is it?
The spermatic cord is a bundle of veins, nerves, and blood vessels that connect the testicles inside the scrotum to the abdomen. Healthy veins in the spermatic cord have valves inside them that circulate blood from the testicles to the scrotum and back to the heart.
In a varicocele, the valves in the vein fail to effectively move blood back to the heart, causing blood to pool in the vein. This results in an enlarged or swollen testicular vein called a varicocele.
Like varicose veins, the exact cause of varicoceles is unknown. While there are no established risk factors for varicoceles, about 15% of adult males and 20% of adolescent males have varicoceles.
Symptoms:
Varicoceles do not always present noticeable symptoms. However, if you have varicoceles you may notice:
- An achy or heavy feeling the scrotum, especially when standing for long periods of time
- Visibly enlarged or gnarled looking veins (some men report these look like a bag of worms)
- Swelling in the testicles
- Tenderness to the touch
A varicocele is rarely a serious health issue. However, if the varicocele is severe it can raise the temperature around the testicle. This lowers sperm production or decreases the quality of sperm. It can also cause testicular atrophy (shrinkage of the testicle) which can compromise sperm production as well. Because varicoceles can affect the quality of sperm, men with varicoceles and fertility issues should talk to their doctor about the best way to deal with this condition.
Diagnosis:
Varicoceles are usually diagnosed through a physical exam where your physician examines you while standing. Your doctor is able to determine whether you have varicoceles from the appearance of your scrotum veins, but may also feel for tenderness. Your physician may also order a scrotal ultrasound to get a detailed picture of your veins and screen for other potential causes of the varicocele.
Treatment:
As mentioned above, varicoceles are rarely a serious medical issue. Your doctor will work with you to determine the severity of your condition and decide what procedure is right for you. For mild cases of varicoceles, doctors will often recommend wearing tight underwear or a jock strap to provide support and lesson painful symptoms. For more severe cases, your doctor may consider treatment options like open surgery or laparoscopic surgery.
Open surgery is the most invasive treatment option with a recovery time of 7 to 10 days, and laparoscopic surgery is slightly less invasive as it only requires a small incision in the abdomen. However, there is another minimally invasive treatment option called varicocele embolization that utilizes imaging technology to see inside the patient.
Interventional Radiologists perform varicocele embolization to treat the malfunctioning vein. This is a less invasive treatment than both open surgery and laparoscopic surgery. Using fluoroscopy (an imaging machine that provides continuous x-ray images) the interventional radiologist inserts a small catheter through a very small incision into the the femoral artery, jugular vein, or arm vein. The catheter is then guided into to the affected testicular vein. The interventional radiologist then either places a small coil into the vein to block blood flow or injects a medicine which causes the vein to close up.
This causes blood to reroute to nearby healthy veins, flowing more efficiently through the scrotum and back to the heart. Over a few weeks, the body reabsorbs the treated vein and it disappears.
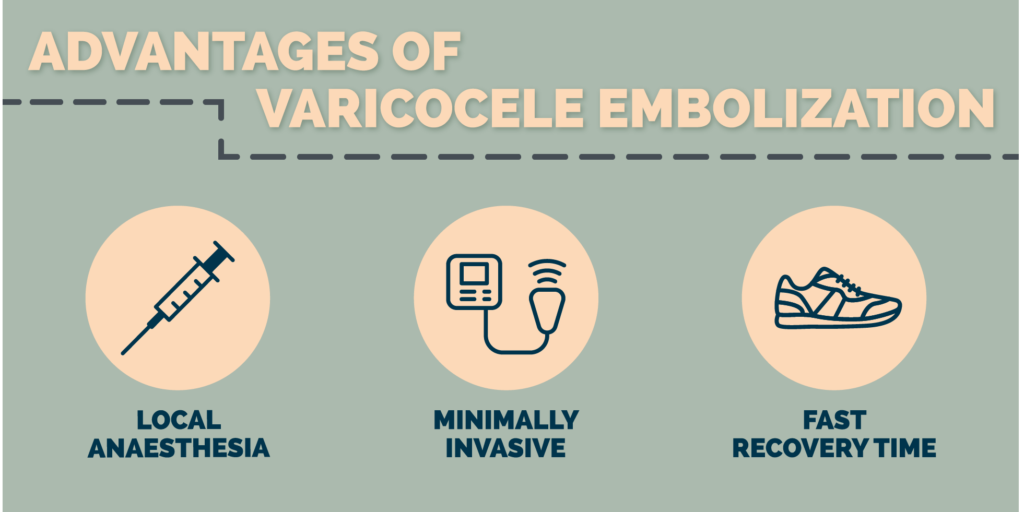
3 Advantages of Varicocele Embolization
- This procedure uses local anesthetics combined with IV sedatives rather than general sedation.
- It is a much less invasive procedure since it only involves making a slight incision in the skin and uses imaging-guidance to move the catheter towards the enlarged vein.
- Recovery time is much shorter as well due to the less invasive nature of the procedure. Most patients are able to resume normal activities within 24 hours.
UVA Interventional Radiology’s team of skilled providers are able to screen for varicocele and provide minimally invasive treatment like varicocele embolization. If you notice these symptoms, including the appearance of large veins in your scrotum, call 434-924-9401 to schedule a consultation.